Criminal Convictions can have serious consequences on peoples’ lives – especially non-citizens who wish to stay in the United States. Many immigration benefits have criminal bars, meaning that certain convictions will prevent you from getting a lawful immigration status, like permanent residence (green card). This Community Explainer offers some options for those who have had certain convictions related to domestic violence or human trafficking, with insights about how to define these crimes, some example scenarios, and explanations about the benefits of a legal tool called a “vacatur.”
This downloadable flyer is designed to raise awareness about the misinformation that often circulates in the undocumented community about the viability of qualifying for lawful permanent resident status solely for having lived in the U.S. for at least 10 years.

If you are hoping to attain lawful permanent resident status (getting a green card) or apply for an immigrant visa as a “child” and your 21st birthday is coming up, read this Community Alert to learn about how changes to USCIS’ interpretation of a law called the Child Status Protection Act might impact you.
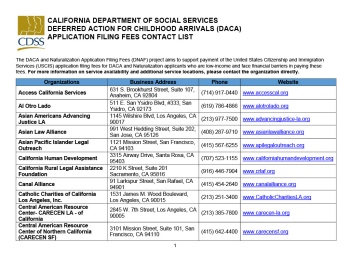
If you are a DACA recipient living in California and facing financial challenges, you can get your renewal filing fees covered by connecting with and getting support from a participating direct services organization found in the directory below. Note that this support is only available until the end of 2023.
On May 11, 2023, the Biden administration issued a new regulation creating a bar to asylum for people arriving at the southern U.S. border with certain narrow exceptions. Although there is an ongoing court challenge, the bar, known as the “lawful pathways” rule, remains in effect. This Community Alert explores the exceptions to the bar with a focus on some of the exceptions that apply to children and youth traveling with their families.
In December 2022 USCIS announced that it was starting a pilot project to redesign the English/civics test for naturalization. If the pilot test is adopted, applicants will face a more difficult English/civics exam. This community explainer breaks down some of those challenges, and how advocates can push for a more inclusive process of naturalization.

In June 2023, the California Dignity Not Detention Coalition passed a budget initiative in California called HEAL (Healthy Economies Adapting to Last). HEAL dedicates 5 million dollars to incentivize California localities to divest from immigration detention by providing them funding to invest in new industries and jobs. HEAL presents a new tool in our advocacy toolbox to close detention centers once and for all. This community FAQ breaks down Dignity not Detention’s newest initiative.
This guide walks through the latest updates regarding TPS for immigrants from El Salvador, Honduras, Nepal, and Nicaragua. Included are frequently asked questions about the program, renewal timelines, and more.
This Community Explainer is designed to explain what an ITIN is, why it may be particularly important for immigrants without a Social Security Number, and how one can be obtained.
There is a new law in California that went into effect in 2023 called the California Clean Slate Act (SB 731). Under the Clean Slate Act, authorities will automatically expunge – or dismiss – certain arrests and criminal convictions. While expungement provides relief in the California state criminal legal system, it does not provide the same relief in the immigration context. This explainer walks through some key points about this new law and its implication for immigrants with prior contact with law enforcement.